How 60-Year-Olds Reverse Muscle Loss with ‘Eccentric Training’—10 Slow-Motion Strength Hacks
Tired of watching your muscles fade with each passing year. Many seniors feel trapped in a cycle of weakness, believing strength loss is inevitable after 60.
But what if conventional wisdom about aging and muscle loss has been wrong all along. Enter eccentric training: the breakthrough method that’s transforming lives through controlled, slow-motion movements.
Thousands of seniors have already discovered this gentle yet powerful approach to rebuilding lost muscle. Right now, you can join them with these 10 revolutionary strength-building techniques that work specifically for your body.
1. Reverse Push-Ups: Tricep Deceleration Mastery
The reverse push-up represents an innovative approach to upper body strength development that specifically targets the triceps through controlled eccentric movement.
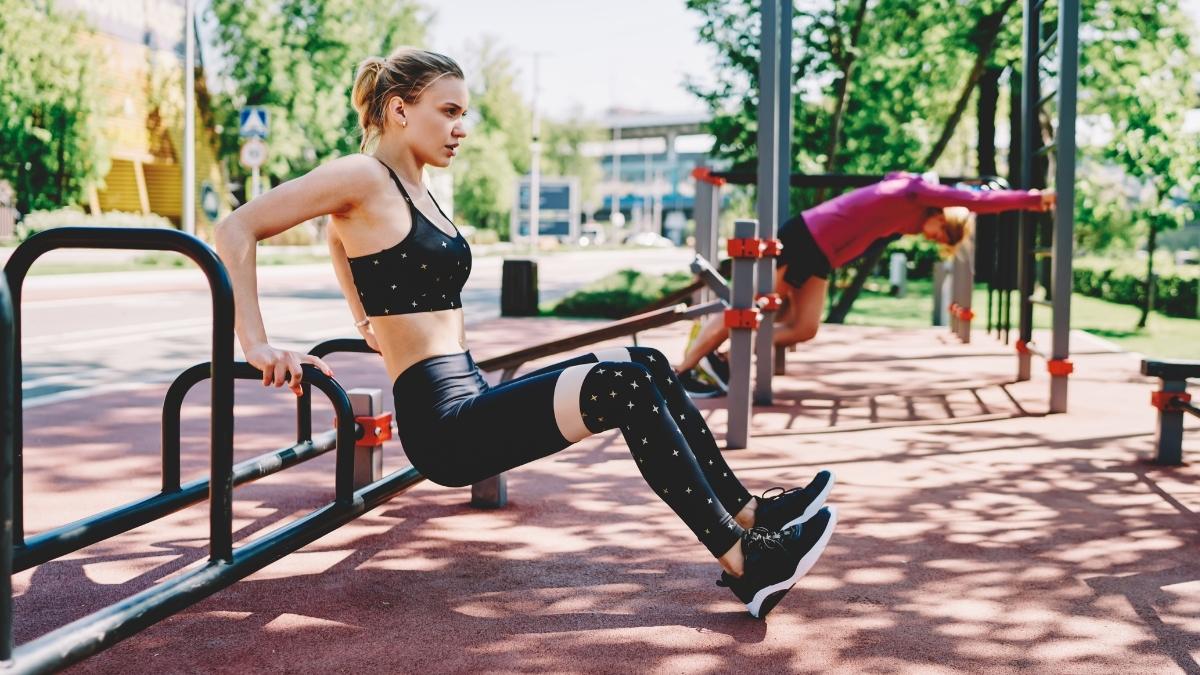

This exercise uniquely combines traditional strength training principles with yoga-inspired body awareness, making it particularly effective for developing muscular control and joint stability. The four-second descent creates significant time under tension, allowing for enhanced muscle fiber recruitment and improved proprioception.
By incorporating a one-second pause at the bottom position, this exercise develops strength in a traditionally weak position while promoting shoulder stability and scapular control.
- Always maintain a neutral spine position throughout the movement
- Begin with wall push-ups if the standard floor version is too challenging
- Focus on even weight distribution between both hands
- Breathe steadily throughout the descent phase
- Keep elbows close to the body to maximize tricep engagement
2. Reverse Pull-Ups: Negative Grip Supremacy
The reverse pull-up technique revolutionizes traditional pull-up training by emphasizing the eccentric phase of the movement, making it particularly beneficial for individuals working towards their first full pull-up or those managing joint sensitivity.
This exercise capitalizes on the body’s greater strength capacity during eccentric contractions, allowing for effective upper body development even without the ability to perform standard pull-ups.
The extended lowering phase of 5-7 seconds creates substantial muscular tension, promoting strength gains while minimizing joint stress.
- Start with assisted variations using resistance bands if needed
- Maintain tension throughout the entire descent
- Focus on feeling the shoulder blades move during the lowering phase
- Keep core engaged to prevent excessive swinging
- Progress by increasing time under tension before adding weight
3. Reverse Split Squats: Quadriceps Lengthening
This advanced variation of the traditional split squat focuses on controlled eccentric loading of the quadriceps, making it particularly valuable for developing lower body stability and strength.

The three-second descent protocol ensures proper muscle engagement while promoting balance and proprioception.
By mimicking the biomechanics of descending stairs, this exercise directly translates to improved functional mobility and reduced fall risk in daily activities.
- Start with bodyweight before progressing to weighted variations
- Keep front foot firmly planted throughout the movement
- Maintain upright posture and engage core throughout
- Focus on controlling the descent rather than the ascent
- Use mirrors initially to check form and alignment
4. Single-Leg Romanian Deadlifts: Posterior Chain Control
The single-leg Romanian deadlift represents a sophisticated approach to posterior chain development, combining elements of balance training with targeted hamstring and glute activation.
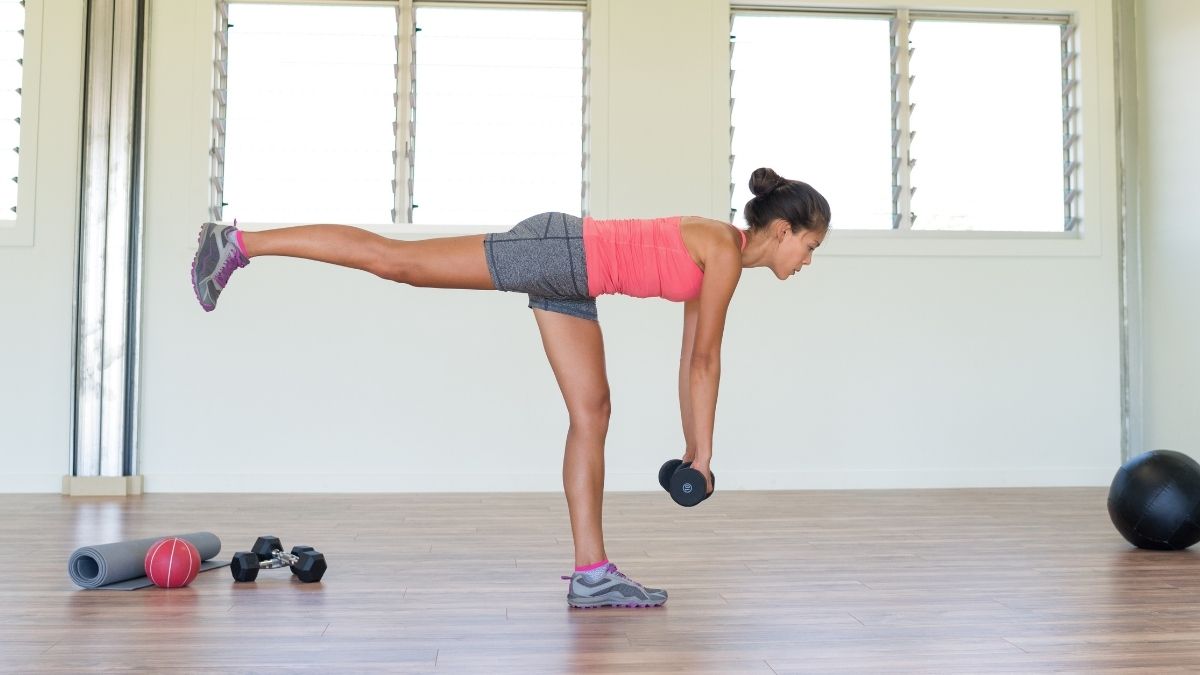

The four-second lowering phase coupled with a two-second hold at the bottom position creates an intense stimulus for muscle growth and neural adaptation.
This exercise excels at developing proprioception and single-leg stability while simultaneously strengthening the entire posterior chain.
- Begin with no weight to master the hip hinge pattern
- Keep the standing leg slightly bent throughout the movement
- Focus on maintaining a neutral spine position
- Progress to unstable surfaces only after mastering stable ground
- Use mirror feedback to ensure proper alignment
5. One-Legged Hop & Hold: Explosive Absorption
This dynamic exercise combines plyometric power with stability training, creating an effective method for developing quick-reaction strength and balance control.
The two-second hold requirement after each hop develops the crucial skill of force absorption, which is essential for preventing falls and maintaining stability during unexpected movements.
The diagonal movement pattern challenges proprioception in multiple planes, making it particularly effective for developing functional agility and coordination.
- Start with small, controlled hops before increasing distance
- Land softly on the mid-foot to properly absorb impact
- Keep eyes focused forward to maintain balance
- Ensure knee tracks over toes during landing
- Progress to multi-directional hops only after mastering forward jumps
6. Stair Calf Lowers: Achilles Strengthening
The stair calf lower exercise provides a unique approach to ankle and calf complex strengthening by emphasizing the eccentric phase of the movement. The five-second lowering protocol allows for deep stretching and strengthening of the Achilles tendon while promoting ankle mobility and stability.
This exercise is particularly effective at preventing age-related tendon stiffness and maintaining lower leg function.
The movement pattern directly translates to improved balance and stability during walking and running activities, making it an essential exercise for maintaining functional mobility.
- Ensure heel drops below step level for full range of motion
- Keep ankle aligned throughout the movement
- Use both legs to rise, one leg to lower for proper loading
- Maintain slight knee bend to protect joints
- Progress to single-leg variations gradually
7. Squat Pulse Hypertrophy Technique
This innovative squat variation introduces micro-pulsing movements at the bottom position to maximize muscle fiber recruitment and time under tension.
The three-second descent combined with three pulses and two-second ascent creates an intense stimulus for muscle growth while improving stability and control throughout the movement pattern.
This technique is particularly effective at combating age-related muscle loss by increasing metabolic stress and mechanical tension on the working muscles. The pulsing movement also helps develop better awareness of proper positioning and engagement patterns.
- Focus on maintaining consistent depth during pulses
- Keep weight distributed evenly through entire foot
- Coordinate breathing with movement pattern
- Engage core throughout entire movement
- Start with bodyweight before adding external load
8. Eccentric Seated Leg Press
The eccentric seated leg press provides a controlled environment for developing lower body strength while minimizing risk of injury.

The six-second lowering phase creates significant time under tension, allowing for maximal muscle fiber recruitment and strength development.
This machine-based exercise is particularly valuable for rehabilitation purposes and for individuals who need to develop baseline strength before progressing to free-weight exercises.
- Start with light weights to master the tempo
- Keep feet positioned shoulder-width apart
- Maintain constant tension throughout movement
- Never lock knees at top of movement
- Progress weight gradually while maintaining form
9. Resistance Band Eccentric Rows
The resistance band eccentric row offers a joint-friendly approach to upper body pulling strength development.

The four-second release phase ensures proper engagement of the posterior shoulder muscles while promoting scapular stability and control.
This exercise is particularly effective for maintaining shoulder health and preventing rotator cuff issues. The variable resistance provided by the band creates a unique stimulus that helps develop control throughout the entire range of motion while minimizing joint stress.
- Keep shoulders depressed throughout movement
- Focus on squeezing shoulder blades at end of pull
- Maintain neutral wrist position
- Control the entire releasing phase
- Progress by using stronger resistance bands
10. Slow-Motion Farmer’s Carry Lower
This advanced variation of the traditional farmer’s carry emphasizes the often-neglected lowering phase of the movement, creating a unique stimulus for grip strength and core stability.

The five-second controlled drop challenges the entire body’s ability to maintain proper positioning while managing heavy loads. This exercise particularly excels at developing real-world strength and control, making it valuable for both athletic performance and daily function.
- Start with lighter weights to master controlled lowering
- Maintain proper posture throughout carry and lower
- Keep core engaged during entire movement
- Focus on even lowering between both sides
- Progress weight only when control is maintained
Final Thoughts
Eccentric training’s dual benefits—muscle hypertrophy and tendon resilience—make it a game-changer for seniors. By prioritizing slow, controlled movements, 60-year-olds can rebuild strength without joint strain.
Studies show even once-weekly sessions yield significant gains, making it a sustainable strategy 7. Pair these hacks with adequate protein intake and recovery days for optimal results. Remember: “Slow is the new strong” when reversing muscle loss.
Pro Tip: Track progress with a training journal—note tempos, weights, and stability improvements to stay motivated!







